Assignment
See Corresponding Assignment
Module 7 GCD Assignment
Background and why we're covering it
Channel geometry refers to the three dimensional form of the channel, which we capture quantitatively with topographic surveys. The net change in topography from erosion and deposition through time are channel adjustments and we will explore how we measure and quantify those adjustments.
Learning Outcomes
-
LO 1. Confidently read any riverscape and be able to map its core characteristics.
-
LO 2. Differentiate influence of external controls (e.g., climate and catchment) vs. local controls on form and process.
-
LO 3. Apply principles of geomorphic analysis to a diversity of riverscapes.
-
LO 4. Recognize the primary controls on riverscape diversity, in which distinctive suites of physical and biotic processes (behavior) help shape the form and character of those landscapes.
-
LO 5. Appreciate that topography is a quantitative record of landforms and apply morphometric analysis can be used to map and differentiate those landforms (i.e., geomorphic units).
Resources
Part 1 - Intro + Bed & Bank Processes that Influence Channel Shape
Lecture
⏱️ 1:05 hours.
Slides
Slides
Lecture Slides - Module 7 (Part 1)
Part 1 - Channel Geometry - Topography
Part 2 - Channel Shape & Hydraulic Geometry
Lecture
⏱️ 37 minutes.
Slides
Slides
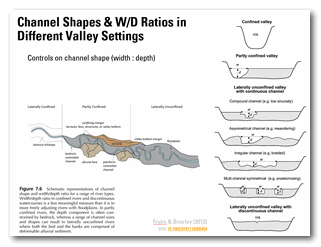
Lecture Slides - Module 7 (Part 2)
Part 2 - Channel Geometry - Topography
Part 3 - Topographic Surveys, Geomorphic Change Detection and your Homework
Lecture
⏱️ 37 minutes.
Slides
Slides
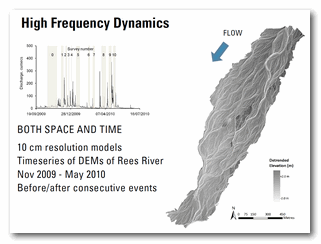
Lecture Slides - Module 7 (Part 3)
Part 3 - Channel Geometry - Topography
Related Reading
This module focus on: CHAPTER SEVEN: Channel geometry from:
- Fryirs KA, Brierley GA. 2013. Geomorphic Analysis of River Systems: An Approach to Reading the Landscape, First Edition. Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Chichester, U.K.
Other Resources
- See Riverscapes Consortium
- See Capstone
- See GUT
- See GCD